网站建设进度表求几个微信推广平台
一、介绍
在C语言中,UTC(协调世界时)时间戳与北京时间(通常指中国标准时间,即东八区时间,UTC+8)之间的转换,主要涉及到将UTC时间戳加上8小时的时差(忽略夏令时等复杂因素)。
首先,需要了解的是,时间戳是自1970年1月1日(UTC)以来的秒数。在C语言中,可以通过time()函数 或者 gettimeofday() 获取当前时间的UTC时间戳,然后可以通过添加相应的秒数来转换为北京时间。
二、示例
下面是一个简单的示例代码,展示了如何将UTC时间戳转换为北京时间,并以YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS的格式打印出来。为了简化示例,这里使用了gmtime(将时间戳转换为UTC时间)和 localtime(将时间戳转换为本地时间,这里假设本地时间是北京时间)来演示,但实际上,直接通过添加时差来转换更为直接和明确。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h> #define BST (+1)
// 将UTC时间戳转换为北京时间并打印
void print_beijing_time(time_t utc_timestamp)
{ // 转换为北京时间(UTC+8) time_t beijing_timestamp = utc_timestamp + 8 * 60 * 60; // UTC+8小时 printf("utc_timestamp= %ld\r\nbeijing_timestamp= %ld\r\n",utc_timestamp,beijing_timestamp);// 转换为本地时间结构体(这里假设本地时间是北京时间) struct tm *beijing_time = localtime(&beijing_timestamp); // 打印时间 printf("%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", beijing_time->tm_year + 1900, // 年份从1900年开始 beijing_time->tm_mon + 1, // 月份从0开始 beijing_time->tm_mday, // 日 beijing_time->tm_hour, // 小时 beijing_time->tm_min, // 分钟 beijing_time->tm_sec); // 秒
} int main(void)
{ struct tm *info;// 获取当前UTC时间戳 time_t now = time(NULL); /* Get GMT time */info = gmtime(&now );printf("Current world clock:\n");printf("UTC :\r\n");printf("%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", info->tm_year + 1900, // 年份从1900年开始 info->tm_mon + 1, // 月份从0开始 info->tm_mday, // 日 info->tm_hour, // 小时 info->tm_min, // 分钟 info->tm_sec); // 秒 printf("London : %2d:%02d\n", (info->tm_hour+BST)%24, info->tm_min);// 打印北京时间 print_beijing_time(now); return 0;
}
三、strftime函数的使用

C 库 strftime() 函数用于将日期和时间格式化为字符串。它允许用户设置自定义的日期和时间表示。
size_t strftime(char *str, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *timeptr)
可以根据格式中定义并存储到 str 中的格式规则,格式化结构 timeptr 中表示的时间。
参数介绍
str − This is the pointer to the destination array where the resulting C string is copied.
maxsize − This is the maximum number of characters to be copied to str.
format − This is the C string containing any combination of regular characters and special format specifiers. These format specifiers are replaced by the function to the corresponding values to represent the time specified in tm. The format specifiers are −
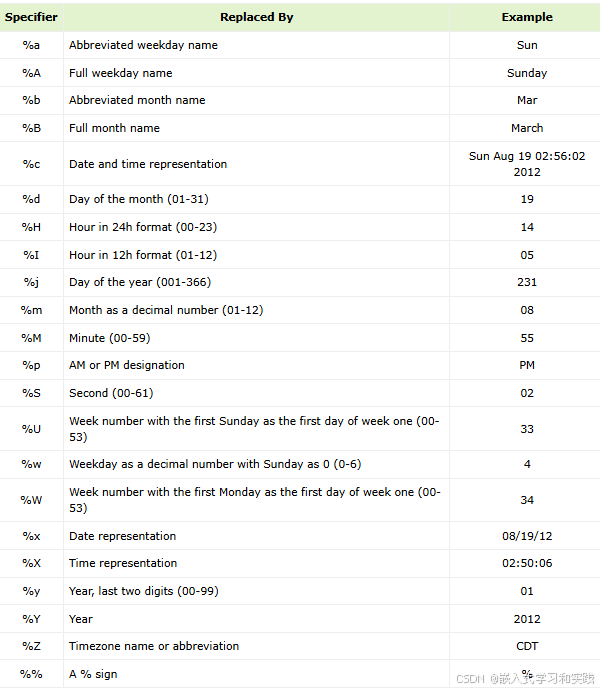
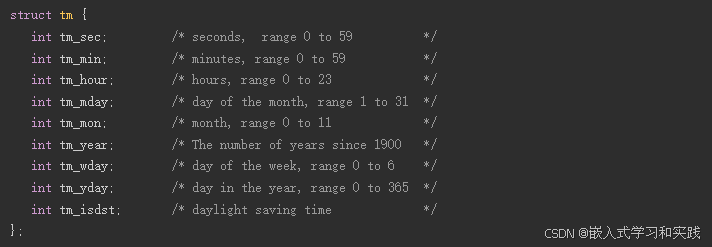
timeptr − This is the pointer to a tm structure that contains a calendar time broken down into its components as shown below −
示例1:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>int main () {time_t rawtime;struct tm *info;char buffer[80];time( &rawtime );info = localtime( &rawtime );strftime(buffer,80,"%x - %I:%M%p", info);printf("Formatted date and time : |%s|\n", buffer );return(0);
}
效果:
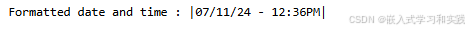
示例2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define Size 50int main() {time_t t;struct tm *tmp;char MY_TIME[Size];// Get the current timetime(&t); // Convert to local timetmp = localtime(&t); // Format the date and timestrftime(MY_TIME, sizeof(MY_TIME), "%x - %I:%M%p", tmp);printf("Formatted date & time: %s\n", MY_TIME);return 0;
}
效果:
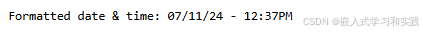
示例3:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>int main()
{time_t anytime;struct tm *current;char time_str[64];time(&anytime);current = localtime(&anytime);strftime(time_str, 64, "%A, %B %d, %Y", current);printf("Today is %s\n", time_str);return 0;
}
效果:
参考:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/c_standard_library/c_function_strftime.htm
